What is Product Management?
Product management has become an increasingly prevalent role but what exactly does it entail? Read this guide to find out more about the industry and tips for breaking in.
Posted July 9, 2025

Join a free event
Learn from top coaches and industry experts in live, interactive sessions you can join for free.
Table of Contents
What is Product Management?
Product management has become an increasingly prevalent role but what exactly does it include? Read this guide to find out more about the industry and tips for breaking in.
Product management is an organizational role responsible for guiding a product through every stage of its lifecycle. A product manager is the person on the team who ensures the product meets both customer needs and business objectives by collaborating with cross-functional teams, including engineering, design, marketing, and sales teams. The product management process combines strategic planning, user research, and hands-on involvement in the development process to create products that customers love.
A product manager's job is to act as the bridge between the product team and the rest of the organization. They define the product vision, align it with business goals, and ensure the entire organization is on the same page throughout the product lifecycle. This role requires a balance of technical skills, soft skills, and a deep understanding of the target market.
Core Responsibilities of a Product Manager
While the specific responsibilities may vary depending on the company, the key components of a successful product manager's role include:
Conducting Research:
Product managers gain a deep understanding of their target market by doing market research, analyzing customer behavior, and identifying pain points. This research informs the product’s direction and ensures alignment with market demands.
Developing a Product Strategy:
A product manager defines a roadmap based on user feedback, business objectives, and technical specifications. This involves prioritizing product features and developing a business case for proposed solutions.
Collaborating with Cross-Functional Teams:
Product managers work with development teams, marketing teams, and sales teams to execute the product roadmap. They ensure that all teams are aligned and working toward a unified vision.
Acting on Feedback and Data Analysis:
By gathering customer feedback and analyzing key metrics, product managers identify areas for improvement and iterate on the product to better meet user needs. This iterative process is crucial for driving a product's success.
Driving Product Development:
Product managers guide the development process, ensuring that technical product managers, designers, and engineers stay on track to deliver high-quality products. Tools such as Jira and Trello are often used to manage the workflow.
What Does A Product Manager Actually Do?
To understand what a product manager does, it's important to recognize that the role varies depending on the industry and product; however, there are some tasks that are universal. PMs are the “product owners” because they have responsibility for a product and work closely with every part of the company tasked with releasing and maintaining a successful product. A product manager defines crucial elements such as the minimum viable product (MVP) and testing scenarios during development, ensuring that their definition encompasses planning, communication, and adaptability based on user feedback.
The product manager's job involves strategizing and developing products that meet user needs, making critical decisions on which features to implement next, and ensuring these align with the overall product strategy.
Responsibilities of A Product Manager
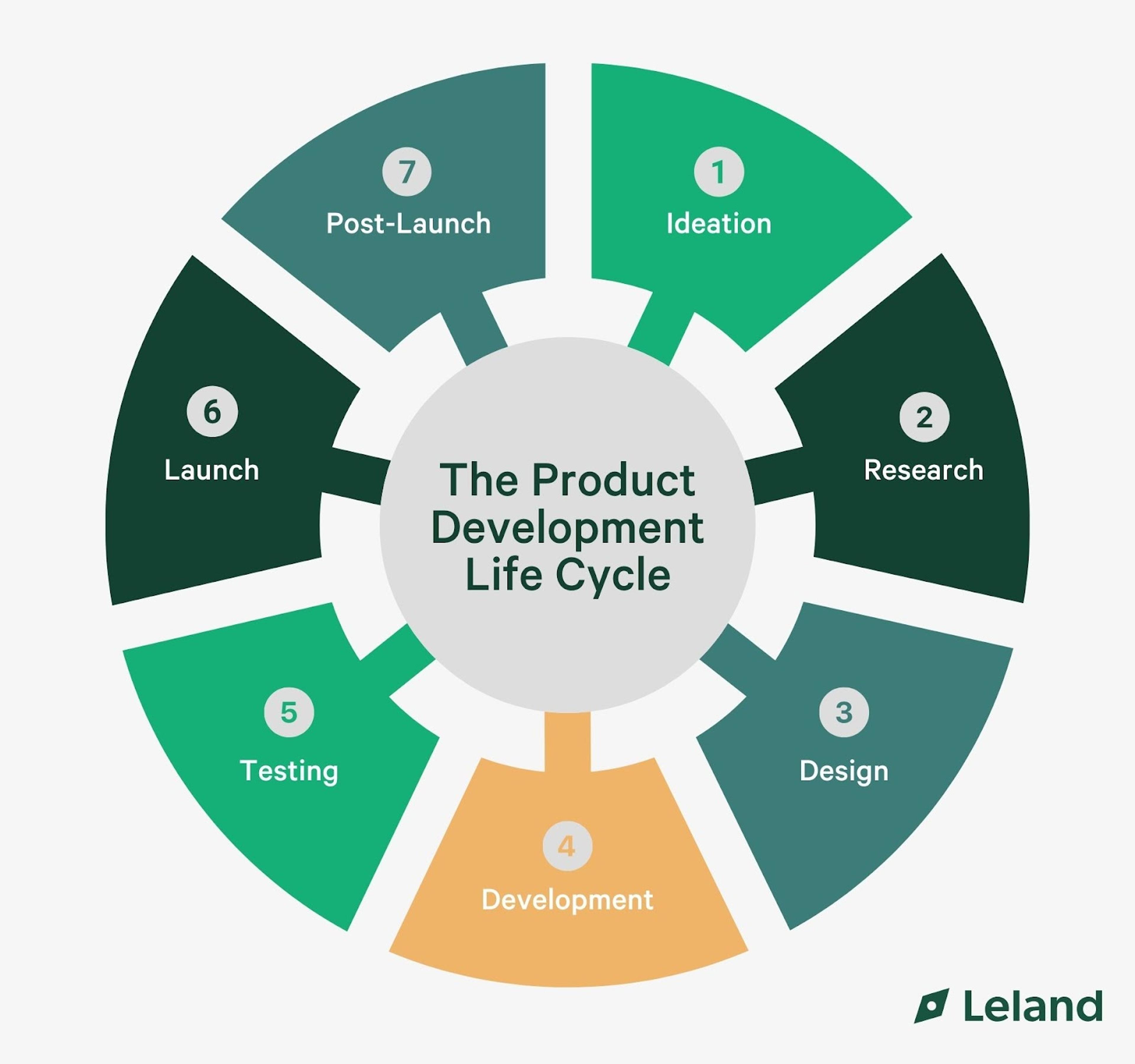
Product managers (PMs) are responsible for defining the product vision, conducting market research, and ensuring the product meets customer needs while aligning with the company’s business objectives. PMs work with cross-functional teams like engineering, design, and marketing to ensure smooth execution at every stage of the product development process.
This involves gathering and analyzing customer feedback, defining the product roadmap, and continuously refining the product to stay ahead of market demands and user expectations. Let’s explore the core responsibilities of a product manager and how they contribute to a product’s success.
1. Conduct market and product research
PMs are hired, in part, because of their expertise in a certain industry and product. This is necessary because it allows them to see the entire lifecycle of a product and plan accordingly. They need a solid understanding of the competition, market innovation, major players, and the industry’s financial health. This is also important because they’re better able to preempt and respond to customer feedback, both positive and negative.
2. Define the product roadmap
The PM is in charge of laying out the workflow for a project, including the specificities of features, the work distribution across different teams, and timelines for release. Basically, PMs are tasked with making sure that each part of the business is working on the right things at the right time and in the right order. Product strategy is important because it provides everyone in the organization with a map to success and a unified vision.
3. Analyze customer needs and collect feedback
In order to release the best product possible, PMs must interact often with customers to get feedback and identify pain points. With market knowledge and this feedback, the product managers will be able to anticipate future issues and interpret the feedback that they do get. PMs need to fully understand why the customers are buying–or not buying–their product (or a similar product) and what could make it better.
4. Test the product
After developing a beta version of the product, PMs are also responsible for testing it, identifying potential problems, and coming up with solutions. Through data analysis and customer surveys, the success of the product will be measured and any necessary revisions planned. The PM is also the person responsible for conveying the progress of the product to the business leaders and making sure that all teams continue to stay on track with the roadmap.
How to Create a Product Strategy as a Product Manager
The product manager's responsibilities include setting the vision, developing strategies, prioritizing customer needs, facilitating cross-functional team collaboration, and ensuring that the product aligns with business goals and customer expectations. Because of the product’s cruciality to the overall success of the company, creating a strategy for it can be an intimidating and difficult task. Here, we’ve outlined the steps to a successful strategy.
1. Understand the Problem and Audience:
First and foremost, it’s important to determine exactly what the problem is that your product will solve and who it will solve it for. Both of these are required for any of the steps after because they will change the overall vision. Also, keeping the problem and audience in mind will help PMs anticipate pain points, identify solutions, and stay focused.
2. Specify the Vision:
A product’s vision is a high-level understanding of where the product is going. Put differently, it’s the reason for the product. Recognizing the reason, and hence the vision, will help the PMs create a better product-market fit and make sure that the product meets its long-term goals. Part of specifying the vision is also communicating it to every part of the organization in order to ensure that the entire employee body is working together towards a unified goal.
3. Create the Product Designs:
Now that you have an idea of the problem you’re solving and the place you’re trying to get to, it’s possible to draft a product design. These designs should help guide the roadmap and address customers’ needs. It’s important that the product designs are synchronized with other parts of the organization so that the individual pieces will come together well in the final product.
4. Implement the Strategy:
After the designs have been developed and communicated, the team will begin to execute the product strategy. This strategy will change as the product moves further along and in accordance with the current vision and goals. It should constantly be evaluated for effectiveness and accuracy.
5. Feedback, Flaws, Fixes:
Depending on the product, the PM will gather feedback on the product at different points in its development. As flaws are identified from research, testing, and customer critiques, the PM will need to work with the different teams on finding and implementing solutions.
Common Challenges in Product Management
Product management is a challenging role that demands strong communication, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. Product managers often navigate complex organizational dynamics, prioritize competing demands, and make tough decisions with limited resources. To overcome these challenges, it’s essential to develop a deep understanding of customer needs and build strong relationships with cross-functional teams.
Staying focused on the product vision and strategy is crucial, as is being adaptable and resilient. Learning from failures and continuously improving are key aspects of a successful product manager’s job. By honing these skills and strategies, product managers can effectively tackle the challenges of product management and drive their products and organizations toward success.
Tips for Getting Into Product Management
Breaking into product management requires a blend of skills across technology, business, and design. Here are some key tips for successfully entering the field:
- Develop Expertise in a Core Area: Product management exists at the crossroads of technology, business, and design. Gain deep expertise in at least one of these areas to establish a solid foundation for success as a product manager.
- Cultivate Product Management Skills: Focus on building key product management skills like leadership, problem-solving, data analysis, and cross-functional collaboration. These are essential for managing the product management process and interacting with development teams.
- Understand the Product Lifecycle: Familiarize yourself with the product's lifecycle from conception to launch. This includes learning about the product roadmap, customer feedback integration, and the role of sales teams in shaping product strategy.
- Enhance Technical and Business Knowledge: Many product manager roles require technical skills, particularly for managing software products. At the same time, having a strong grasp of business objectives, market research, and customer needs is critical to aligning with business goals and developing products that resonate with the target market.
- Leverage Networking and Resources: Join product management groups, attend industry events, and consider product management certification programs to enhance your industry knowledge and connect with other product managers.
- Gain Cross-Functional Experience: Work with cross-functional teams, including sales, engineering, and marketing teams, to understand the full scope of a product manager's responsibilities, from defining product vision to launching successful products.
The Bottom Line
Product management sits at the intersection of strategy, execution, and user empathy. It’s a dynamic role that requires balancing customer needs with business goals, while collaborating across teams to bring ideas to life. Whether you're aiming to break into the field or grow within it, focus on building core skills ike communication, market insight, and problem-solving, and stay curious about how great products are made. With the right mindset and experience, a career in product management is not only possible, but deeply rewarding.
Get Help from an Expert
If you prefer one-on-one coaching for interview prep, resume/cover letter help, or anything else related to product management, browse our coaches here. They come with years of experience in their field and proven track records of success.
Before entering the PM field, evaluate the skills you possess and those you don’t, and work to fill the gaps. Here are some free resources to get you started:
- 20+ Free Product Management Resources
- Tips from an Expert: How to Prepare for Your Product Management Interview
- The 25 Best Entry-Level Associate Product Management (APM) Programs
- How to Build Product Sense as a Product Manager
- The Best Newsletters & Podcasts for Product Management
FAQs
What is product management in simple terms?
- Product management is the process of guiding a product from idea to launch, and beyond. It means figuring out what to build, why it matters, and making sure it solves real problems for users while meeting business goals.
What are the top 3 skills for a product manager?
- The top three skills are:
- Communication – clearly conveying ideas across teams
- Strategic thinking – making smart product decisions
- Customer empathy – understanding user needs and pain points
What is the role of a product manager?
- A product manager defines the product vision, creates the roadmap, and works with teams like engineering, design, and marketing to turn ideas into real products. They're responsible for making sure the product delivers value to both customers and the business.
Do product managers get paid well?
- Yes, product managers are generally well-compensated. Salaries vary by industry and experience, but many PM roles, especially in tech, offer competitive pay, often ranging from $100K to $160K+ annually in the U.S., with higher earnings at senior levels.
Browse hundreds of expert coaches
Leland coaches have helped thousands of people achieve their goals. A dedicated mentor can make all the difference.
























