How to Become an Audiologist: Schooling, Career Path, & Salary
If you’re interested in becoming an audiologist, this step-by-step guide is for you! Learn about the education and training required, licensing and certification processes, and what it takes to succeed in this rewarding career.
Posted July 22, 2025

Join a free event
Learn from top coaches and industry experts in live, interactive sessions you can join for free.
Table of Contents
An audiologist is a healthcare professional who specializes in diagnosing, treating, and managing hearing loss and balance disorders. Most audiologists work in hospitals, clinics, universities, and private practices, providing audiological services to patients of all ages. They help individuals with hearing aids, cochlear implants, and other assistive technologies. To become an audiologist, you need extensive education and training.
The process involves earning a bachelor's degree, which is a foundational step toward becoming an audiologist. Typically, a bachelor's degree in fields like communication sciences and disorders is required for admission into doctoral programs. Afterward, you must complete a doctoral program in audiology (Au.D.) and meet licensure requirements. Aspiring audiologists must also pass the Praxis Examination and gain supervised clinical experience.
This article explains the education pathway, clinical training, licensure requirements, job outlook, and salary expectations for those interested in pursuing a career in audiology.
What Does an Audiologist Do?
Primary Responsibilities
Audiologists specialize in diagnosing, managing, and treating hearing problems and balance disorders in patients of all ages. Their role extends beyond simply fitting hearing aids. They play a crucial role in hearing health care, working with individuals to improve their ability to hear, process sound, and maintain balance.
Key Responsibilities of an Audiologist:
Conducting Hearing Tests and Evaluations
- Perform comprehensive hearing assessments to measure hearing sensitivity, speech recognition, and middle ear function.
- Use specialized diagnostic tools such as audiometers, tympanometers, and otoacoustic emissions (OAE) testing.
- Identify the degree and type of hearing loss, distinguishing between sensorineural, conductive, and mixed hearing loss.
Diagnosing and Managing Hearing Loss
- Evaluate the cause, severity, and impact of hearing loss.
- Determine appropriate treatment options, including hearing aids, cochlear implants, or medical referral.
- Develop rehabilitation plans tailored to individual patient needs.
Fitting and Programming Hearing Aids and Cochlear Implants
- Select and custom-fit hearing aids based on a patient’s hearing profile.
- Adjust device settings to optimize sound clarity and comfort.
- Provide ongoing maintenance and adjustments to ensure proper functioning.
Treating Balance Disorders and Dizziness
- Assess and treat vestibular (balance) disorders, such as vertigo and Ménière’s disease.
- Use videonystagmography (VNG), caloric testing, and rotational chair tests to identify balance issues.
- Design personalized vestibular rehabilitation therapy to help patients regain balance and reduce dizziness.
Providing Audiological Services such as Auditory Rehabilitation
- Help patients adapt to hearing loss through therapy and assistive listening devices.
- Teach speechreading techniques and other communication strategies.
- Offer counseling and education to improve social and emotional adjustment to hearing loss.
Educating Patients on Hearing Conservation and Communication Strategies
- Provide preventative education on noise-induced hearing loss.
- Fit custom earplugs and recommend protective hearing devices for workers in high-noise industries.
- Teach patients and their families about effective communication strategies for daily interactions.
Collaborating with Other Healthcare Professionals
- Work with speech-language pathologists, otolaryngologists (ENT doctors), and neurologists for multidisciplinary patient care.
- Provide expert consultation on complex hearing disorders and cochlear implant candidacy.
- Refer patients to medical professionals when surgical or pharmacological intervention is necessary.
Work Environments
Audiologists work in a variety of medical, clinical, and research settings. Their responsibilities may vary depending on where they practice.
Common Workplaces for Audiologists and Their Roles
| Workplace | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Hospitals | Diagnose and treat hearing and balance disorders for patients in outpatient and inpatient settings. Provide emergency care for sudden hearing loss and work alongside ENT specialists. |
| Private Audiology Clinics | Fit and adjust hearing aids, cochlear implants, and assistive listening devices. Provide ongoing patient care and follow-up visits. |
| Schools & Universities | Work with children who have hearing loss and develop Individualized Education Programs (IEPs). Research hearing disorders and train future audiologists. |
| Research Institutions | Conduct scientific studies on hearing loss, balance disorders, and new treatments. Develop new diagnostic tools and treatment methods. |
| Hearing Aid Companies | Train healthcare professionals on hearing aid technology and fitting techniques. Work on the development and improvement of hearing devices. |
| Veterans Affairs (VA) Clinics | Provide specialized hearing care for veterans exposed to high noise levels in the military. Fit hearing aids and assistive devices for those with service-related hearing loss. |
| Industrial and Occupational Health Programs | Implement hearing conservation programs for industries such as construction, manufacturing, and aviation. Perform hearing screenings for employees exposed to loud noise environments. |
Note: Audiologists also have opportunities to specialize in areas such as pediatric audiology, tinnitus management, vestibular disorders, and forensic audiology.
Educational Requirements to Become an Audiologist
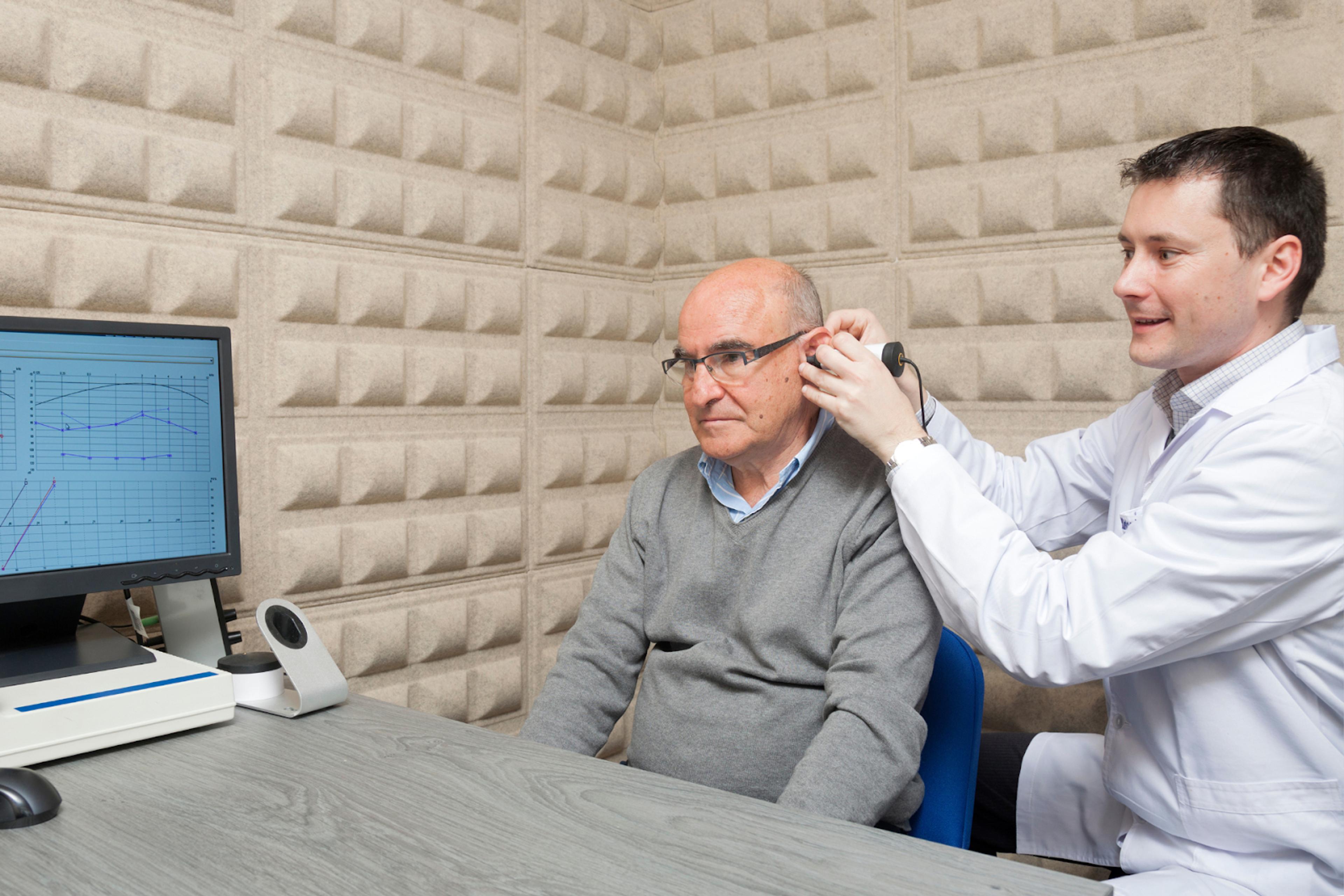
Audiology is a highly specialized healthcare profession that requires extensive education and training. To become an audiologist, students must first complete undergraduate education, followed by a doctoral degree (Au.D.). In addition to coursework, clinical training, and externship experience are required to gain the necessary skills to diagnose and treat hearing and balance disorders.
Bachelor’s Degree
Before applying to an audiology program, students must earn a bachelor’s degree in a related field. While there is no required major, most students choose subjects that provide a strong foundation in science, communication, and healthcare.
Common Undergraduate Majors for Aspiring Audiologists:
- Communication Disorders – Covers topics such as speech and hearing science, language development, and phonetics.
- Biology – Provides an understanding of anatomy, physiology, and neurological functions related to hearing.
- Psychology – Helps students understand cognitive and behavioral aspects of hearing loss and communication disorders.
- Speech-Language Pathology – Focuses on disorders of speech and language, which often overlap with audiology.
Recommended Coursework for Pre-Audiology Students:
Many universities offer pre-audiology tracks, which include courses that prepare students for the rigorous coursework in an Au.D. program. These courses also help students build a working knowledge of the field.
| Course | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| Anatomy & Physiology | Structure and function of the ear, nervous system, and auditory pathways. |
| Physics of Sound | Acoustics, sound waves, and how sound is processed by the auditory system. |
| Statistics & Research Methods | Data analysis, experimental design, and interpretation of audiological studies. |
| Neuroscience | Understanding the auditory nervous system and neurological disorders affecting hearing. |
| Hearing Science | Fundamentals of hearing mechanisms, auditory processing, and sound perception. |
Note: Students planning to apply to audiology programs should ensure they meet all prerequisite requirements for the programs they are interested in. Each university may have slightly different requirements.
Doctoral Degree in Audiology (Au.D.)
To become a licensed audiologist, students must complete a Doctor of Audiology (Au.D.) program. These programs are accredited by the Council on Academic Accreditation in Audiology and Speech-Language Pathology (CAA-ASHA) and typically last four years.
Structure of an Au.D. Program:
- Classroom Coursework – Covers medical and scientific knowledge related to audiology.
- Clinical Training – Students work directly with patients under supervision.
- Research Component – Some programs require research projects or dissertations.
- Externship – A full-time clinical experience in the final year.
Topics Covered in an Audiology Doctoral Program:
- Hearing Science and Disorders – Study of auditory processing and types of hearing loss.
- Cochlear Implants and Hearing Aids – Training in fitting and programming hearing devices.
- Balance Disorders and Vestibular Assessment – Diagnosis and treatment of dizziness and balance problems.
- Audiological Services in Clinical Practice – Best practices for treating patients.
- Medical and Ethical Considerations in Audiology – Legal and professional standards for audiologists.
| Program Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| Duration | 4 years (Doctoral Degree in Audiology) |
| Coursework | Covers hearing science, diagnostics, treatment, and medical ethics. |
| Clinical Training | Hands-on patient care starts in the first year. |
| Research Component | Some programs require independent research or capstone projects. |
Final Year: Supervised Clinical Experience
The final year of an Au.D. program is dedicated to audiology externships, where students gain full-time clinical experience under the supervision of a licensed audiologist. This externship allows students to apply their knowledge in real-world settings, working with patients to diagnose and manage hearing and balance disorders.
What to Expect During the Externship Year:
- Performing hearing evaluations and balance assessments.
- Gaining experience in cochlear implant programming and hearing aid fittings.
- Working in multidisciplinary teams with speech-language pathologists and ENT doctors.
- Developing patient counseling skills for hearing loss management.
- Learning how to follow professional standards and state licensure requirements.
Common Externship Settings:
| Externship Location | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Hospitals | Work with diverse patients, including those with complex medical conditions. |
| Private Clinics | Gain experience in hearing aid fittings and audiological rehabilitation. |
| Universities | Conduct research and assist in teaching audiology students. |
| Pediatric Centers | Work with infants and children who have hearing loss. |
| Veterans Affairs (VA) Clinics | Provide hearing care for military veterans with noise-induced hearing loss. |
Note: This supervised clinical experience is critical in preparing students for professional practice and meeting licensure requirements. After completing the final year, students are eligible to take the Praxis Examination in Audiology and apply for state licensure.
Licensing and Certification Requirements
Licensure Requirements in Most States
1. Completion of an Accredited Audiology Program
- Aspiring audiologists must earn a Doctor of Audiology (Au.D.) degree from an accredited institution.
- The program must be recognized by the Council on Academic Accreditation in Audiology and Speech-Language Pathology (CAA-ASHA).
2. A Passing Score on the Praxis Exam
- The Praxis Examination in Audiology is a standardized test administered by the Educational Testing Service (ETS).
- Most states require a passing score to verify the candidate’s competence in hearing assessment, balance care, and audiological services.
- Some states require the exam to be passed before applying for licensure, while others allow candidates to take it after completing clinical experience.
3. A Specific Number of Clinical Experience Hours
- Most states require candidates to complete audiology externships in supervised clinical settings.
- Externship hours are built into the final year of the doctoral program, ensuring students gain practical experience in hearing loss treatment, cochlear implant programming, and balance disorder evaluations.
State-Specific Licensing Requirements
Each state has its own licensing board that sets specific requirements, including:
- Renewal periods (typically every 1-2 years).
- Continuing education requirements to maintain licensure.
- Additional state-specific examinations or laws regarding patient care.
To find specific state licensure requirements, candidates should consult:
- The American Board of Audiology (ABA).
- The American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA).
- Their state’s health licensing board.
Optional Certifications for Audiologists
While certification is not mandatory, it can enhance job opportunities, increase credibility, and demonstrate expertise in specialized areas. Many employers prefer or require certified audiologists.
1. American Board of Audiology (ABA) Certification
- This certification demonstrates advanced proficiency in audiological services and professional standards.
- Requirements: Passing an exam, completing continuing education, and meeting clinical practice criteria.
- Benefits: Recognized by hospitals, clinics, and universities as a marker of expertise.
2. Certificate Holder in Tinnitus Management (CH-TM)
- Focuses on assessing and managing tinnitus (persistent ear ringing).
- Recommended for audiologists working with veterans, musicians, and patients exposed to loud environments.
3. Pediatric Audiology Specialty Certification (PASC)
- Specialization for audiologists treating children with hearing and balance disorders.
- Covers pediatric hearing aid fitting, cochlear implants, and early intervention strategies.
- Beneficial for audiologists working in schools, children’s hospitals, and pediatric audiology clinics.
Clinical Experience and Training
Externships and Practical Training
Clinical training is essential for aspiring audiologists to develop real-world skills in diagnosing and treating hearing and balance disorders. It allows students to apply their working knowledge in hospitals, clinics, and research institutions before becoming licensed professionals.
Hands-on Clinical Experience Includes:
- Evaluating patients with hearing loss using audiometric testing and other diagnostic tools.
- Performing audiological services like balance testing for dizziness and vestibular disorders.
- Fitting hearing aids and cochlear implants, adjusting settings based on patient needs.
- Working alongside hearing instrument specialists and speech-language pathologists to provide comprehensive care.
- Learning medical ethics, patient counseling, and best practices in clinical practice.
Expert Tip: Most audiology programs integrate clinical practice early, allowing students to gradually build expertise throughout their doctoral studies.
Importance of Supervised Clinical Experience
Full-Time Externship in the Final Year
- The final year of an Au.D. program includes a full-time externship, where students gain intensive training under licensed audiologists.
- Externships are completed in hospitals, private clinics, universities, and VA healthcare facilities.
- Provides an opportunity to apply professional standards before taking the Praxis Examination.
Benefits of Clinical Experience Before Licensure:
| Benefit | Details |
|---|---|
| Practical Experience | Work directly with patients in diagnosing and treating hearing disorders. |
| Hands-on Learning | Develop skills in cochlear implant fitting, hearing aid programming, and balance testing. |
| Networking Opportunities | Establish professional relationships with mentors and potential employers. |
| Meets Licensing Requirements | Most states require externship hours for licensure eligibility. |
Common Externship Settings for Audiology Students:
| Setting | Clinical Focus |
|---|---|
| Hospitals | Work with ENT specialists, neurologists, and emergency care teams. |
| Private Clinics | Gain experience in hearing aid fitting and patient rehabilitation. |
| Schools | Assist children with hearing loss and learning accommodations. |
| Veterans Affairs (VA) Clinics | Provide hearing care for military veterans with noise-induced hearing loss. |
Note: After completing clinical training, students take the Praxis Exam and apply for state licensure, officially allowing them to practice as licensed audiologists.
Employment Opportunities for Audiologists
Audiology is a growing field with various career paths in healthcare, research, and education. Audiologists work in hospitals, clinics, universities, private practices, and research institutions. Some specialize in specific areas of audiology, such as pediatric care, vestibular disorders, or hearing aid technology.
Types of Jobs for Audiologists
Specializations in Audiology
Audiologists can choose to specialize in different areas based on their interests and expertise. Specializations allow professionals to focus on specific patient populations, treatment methods, and research fields.
| Specialization | Role |
|---|---|
| Pediatric Audiology | Work with infants and children diagnosed with hearing loss. Perform early hearing screenings, fit hearing aids, and assist with speech development. |
| Cochlear Implant Audiology | Fit and program cochlear implants for individuals with severe hearing loss. Work closely with surgeons, patients, and families to ensure successful implantation. |
| Vestibular Audiology | Diagnose and treat balance disorders and dizziness caused by inner ear dysfunction. Perform vestibular assessments and provide rehabilitation therapy. |
| Industrial Audiology | Develop hearing conservation programs for workers in high-noise industries like construction, aviation, and manufacturing. Conduct occupational hearing screenings. |
| Research Audiology | Conduct scientific studies on hearing loss, auditory processing, and new hearing technologies. Work in universities, private research labs, or government agencies. |
| Forensic Audiology | Analyze hearing loss cases for legal proceedings, including workplace injury claims and malpractice lawsuits. |
Common Work Environments for Audiologists
| Work Setting | Primary Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Hospitals | Work with medical teams to diagnose and treat hearing and balance disorders in outpatient and inpatient settings. |
| Private Audiology Clinics | Evaluate hearing loss, fit hearing aids, and provide patient counseling. |
| Schools | Support children with hearing impairments, develop individualized education plans (IEPs), and collaborate with teachers and speech-language pathologists. |
| Veterans Affairs (VA) Clinics | Treat hearing loss and tinnitus in veterans exposed to combat noise and loud environments. |
| Hearing Aid Companies | Train professionals on hearing aid technology and assist in product development. |
| Universities & Research Labs | Conduct studies on audiological treatments and teach audiology students. |
Career Growth and Advancement in Audiology
Experienced audiologists have multiple career advancement opportunities. Many move into research, teaching, administration, or private practice.
Career Paths for Experienced Audiologists:
- Private Practice Owner – Open a private audiology clinic and manage a team of audiologists.
- University Faculty – Teach audiology students and conduct research.
- Hospital Department Director – Oversee audiology departments in medical centers.
- Hearing Aid Technology Consultant – Work with hearing aid manufacturers on device development.
- Government and Public Health Audiologist – Assist in policy-making for hearing health programs.
Expert Tip: Audiologists who obtain additional certifications (e.g., Pediatric Audiology Certification, Certificate Holder-Tinnitus Management) may specialize further and increase their earning potential.
Audiologist Salary and Job Outlook
Average Salary of an Audiologist
Salaries for audiologists vary based on location, experience, and work setting. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the average annual salary for audiologists is $92,620.
Audiologist Salary by Percentile
| Percentile | Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| 10% | $56,090 |
| 25% | $74,440 |
| 50% (Median) | $87,740 |
| 75% | $105,480 |
| 90% | $124,800 |
Highest Paying Work Environments:
- Hospitals and specialty clinics often pay higher salaries.
- Audiologists working in research institutions and government agencies tend to earn above-average wages.
- Salaries are typically higher in urban areas compared to rural locations.
Top-Paying States for Audiologists
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| District of Columbia | $117,540 |
| South Dakota | $108,850 |
| Washington | $108,330 |
| New Jersey | $107,660 |
| Georgia | $106,850 |
Job Outlook for Audiologists
Projected Job Growth: 10% Increase (2023-2033)
The demand for audiologists is expected to grow 10% over the next decade, which is faster than the average for all occupations.
Reasons for Job Growth:
- Aging Population: As the population ages, more individuals experience age-related hearing loss and require audiological care.
- Increased Awareness of Hearing Loss and Balance Disorders: Early diagnosis and intervention for hearing problems have led to greater demand for audiological services.
- Advancements in Hearing Technology: Expanding use of cochlear implants and hearing aids is increasing the need for trained audiologists.
- More Hearing Conservation Programs: Industrial audiologists are needed to implement hearing conservation measures in workplaces with loud environments.
Steps to Become an Audiologist
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Earn a Bachelor’s Degree | Complete an undergraduate degree in communication disorders, biology, psychology, or speech-language pathology. |
| 2. Apply to an Audiology Program | Meet prerequisite coursework requirements and submit applications to Doctor of Audiology (Au.D.) programs. |
| 3. Complete a Doctoral Degree (Au.D.) | A 4-year program that includes classroom instruction, clinical practice, and a final-year externship. |
| 4. Gain Supervised Clinical Experience | Work under a licensed audiologist to develop practical skills before licensure. |
| 5. Pass the Praxis Examination | A standardized test is required for state licensure in most states. |
| 6. Obtain State Licensure | Apply for a state license to legally practice audiology. |
| 7. Obtain Certification (Optional) | Pursue ABA certification or specialty credentials for career advancement. |
| 8. Apply for Jobs | Seek employment in hospitals, clinics, universities, private practice, or research institutions. |
Bottom Line
Audiology is a growing field that offers a stable and rewarding career for those interested in hearing and balance healthcare. Becoming an audiologist requires dedication to education, including earning a bachelor's degree, completing a four-year Doctor of Audiology (Au.D.) program, gaining supervised clinical experience, passing the Praxis Exam, and obtaining state licensure. With an aging population, advancements in hearing technology, and increased awareness of hearing loss, job opportunities for audiologists are expected to expand, with competitive salaries and opportunities for specialization in areas like pediatric audiology, cochlear implants, and vestibular disorders. Whether working in hospitals, clinics, research institutions, or private practice, audiologists play a crucial role in improving patients' quality of life by diagnosing, managing, and treating hearing and balance disorders.
Work with Expert Coaches
Just like the path to becoming an audiologist, getting into medical school requires strategic planning and expert guidance. An admissions coach, including former committee members, helps you craft strong applications, refine personal statements, and prepare for interviews.
Related Article:
- Medical School Application Timeline: The Ultimate Guide
- A Guide to the T20 Medical Schools in the U.S.
- Medical School Application Timeline: The Ultimate Guide
- The Ultimate Guide to the Medical School Application Process
FAQs
Do audiologists go to med school?
- No, audiologists do not attend medical school. Instead, they complete a Doctor of Audiology (Au.D.) program, which is a specialized four-year doctoral degree focused on diagnosing and treating hearing loss and balance disorders. Unlike otolaryngologists (ENT doctors), who attend medical school and complete a surgical residency, audiologists focus on non-surgical treatments, such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, and auditory rehabilitation.
What type of audiologist makes the most money?
- Audiologists specializing in cochlear implants, vestibular disorders, and forensic audiology tend to earn the highest salaries. Additionally, audiologists working in hospitals, research institutions, and private practices often earn more than those in schools or government settings. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the top 10% of audiologists make over $124,800 per year, with higher salaries in states like California, Washington, and New Jersey.
Do you need a PhD to be an audiologist?
- No, a Ph.D. is not required to become an audiologist. Instead, aspiring audiologists complete a Doctor of Audiology (Au.D.) degree, which is a clinical doctorate rather than a research-based Ph.D. The Au.D. program includes coursework, clinical experience, and a final-year externship to prepare graduates for licensure and professional practice. However, a Ph.D. in Audiology is an option for those interested in teaching or research.
Is it hard to become an audiologist?
- Becoming an audiologist requires years of education and training, but it is manageable for students who are dedicated to the profession. The path includes four years of undergraduate studies, four years in an Au.D. program, and a full-time clinical externship. While the coursework in hearing science, balance disorders, and medical diagnostics can be challenging, students who are passionate about helping patients with hearing loss find the career highly rewarding.
Browse hundreds of expert coaches
Leland coaches have helped thousands of people achieve their goals. A dedicated mentor can make all the difference.

















